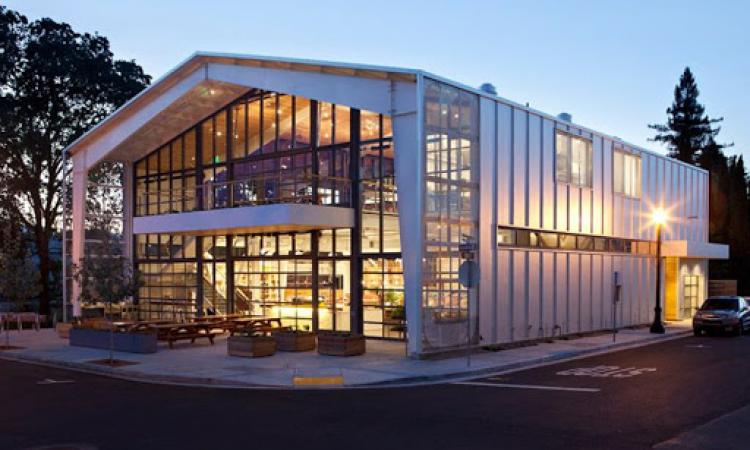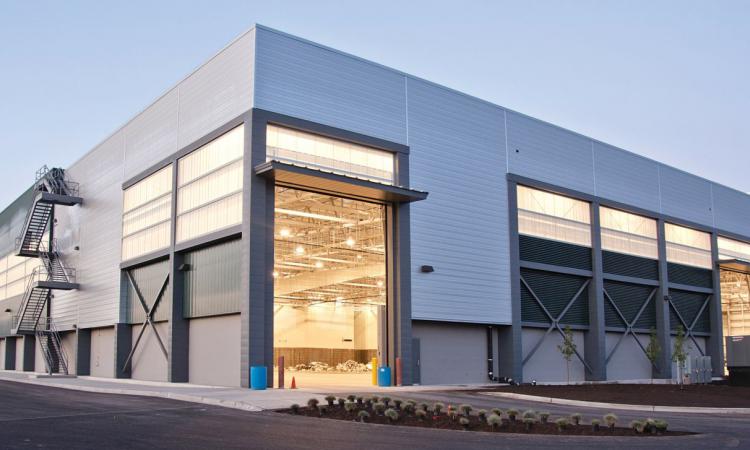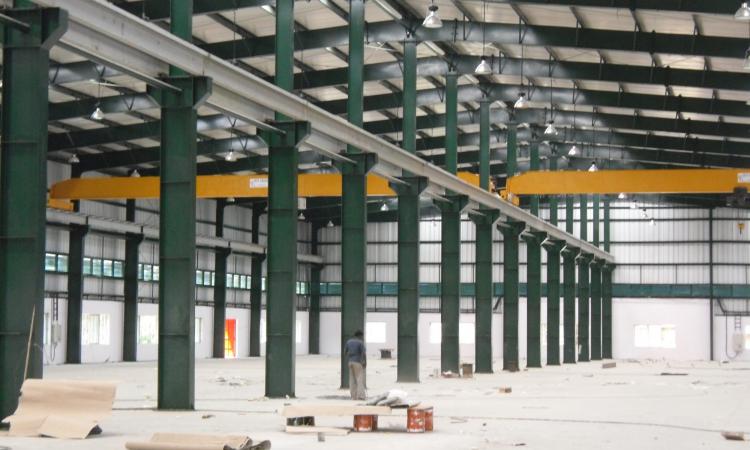
Basic Building Parameters
The PEB Steel Structure of a building comprises of interior rigid frames, endwall bearing or rigid frames, endwall wind columns, secondary structural members (roof purlins & wall girts), wind bracing components and the structural framing of optional subsystems such as roof monitors, mezzanines (inclusive of mezzanine deck and deck fasteners), roof extensions, canopies, fascias, parapets, interior partitions, roof &wall framed openings, anchor bolts, connection bolts and sag rods.
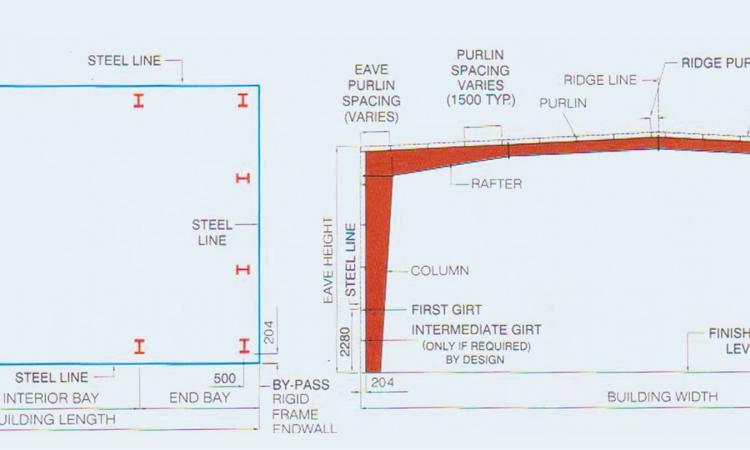
Building width : No matter what primary framing system is used, the building width is defined as the distance from outside of eave strut/Purlin of one sidewall to outside of eave strut of the opposite sidewall.
Building Length : For flush endwalls, the distance between the outside flanges of endwall columns in opposite endwalls is considered the building length. For by-pass endwalls the distance between the outside of wall girts in opposite endwalls is considered the building length. Building lengths is the sum of all bay lengths. For maximum economy maintain equal interior bay length and make the end bays shorter than the interior bays. An example would be a 100 m long building that has 11 interior bay lengths of 8 m and 2 end bay length of 6 m.
Roof Slope (x/10) : This is the angle of the roof with respect to the horizontal. The most common roof slopes is 1/10. Any practical roof slope is possible.
Interior Bay length : Interior bay length is the distance between the center lines of columns of two adjacent interior rigid frames. The most common interior bay lengths in the PEB industry are 6,7.5.8,9 and 10m. The most economical range of interior bay lengths is 7.5-8.5m
Building width : No matter what primary framing system is used, the building width is defined as the distance from outside of eave strut/Purlin of one sidewall to outside of eave strut of the opposite sidewall.
Building Length : For flush endwalls, the distance between the outside flanges of endwall columns in opposite endwalls is considered the building length. For by-pass endwalls the distance between the outside of wall girts in opposite endwalls is considered the building length. Building lengths is the sum of all bay lengths. For maximum economy maintain equal interior bay length and make the end bays shorter than the interior bays. An example would be a 100 m long building that has 11 interior bay lengths of 8 m and 2 end bay length of 6 m.
Roof Slope (x/10) : This is the angle of the roof with respect to the horizontal. The most common roof slopes is 1/10. Any practical roof slope is possible.
Interior Bay length : Interior bay length is the distance between the center lines of columns of two adjacent interior rigid frames. The most common interior bay lengths in the PEB industry are 6,7.5.8,9 and 10m. The most economical range of interior bay lengths is 7.5-8.5m